What are Last Mile Reassembly Attacks?
Last Mile Reassembly Attacks (LMR) refer to a type of cyberattack where the malicious components are assembled directly in the victim's browser from seemingly non-malicious data. This means that the attack payload is not fully formed until it reaches the final stage (the "last mile")—the victim's browser—bypassing traditional network-based detection mechanisms used by cloud proxies, including Secure Web Gateways (SWGs).
Why is Last Mile Reassembly dangerous to enterprises?
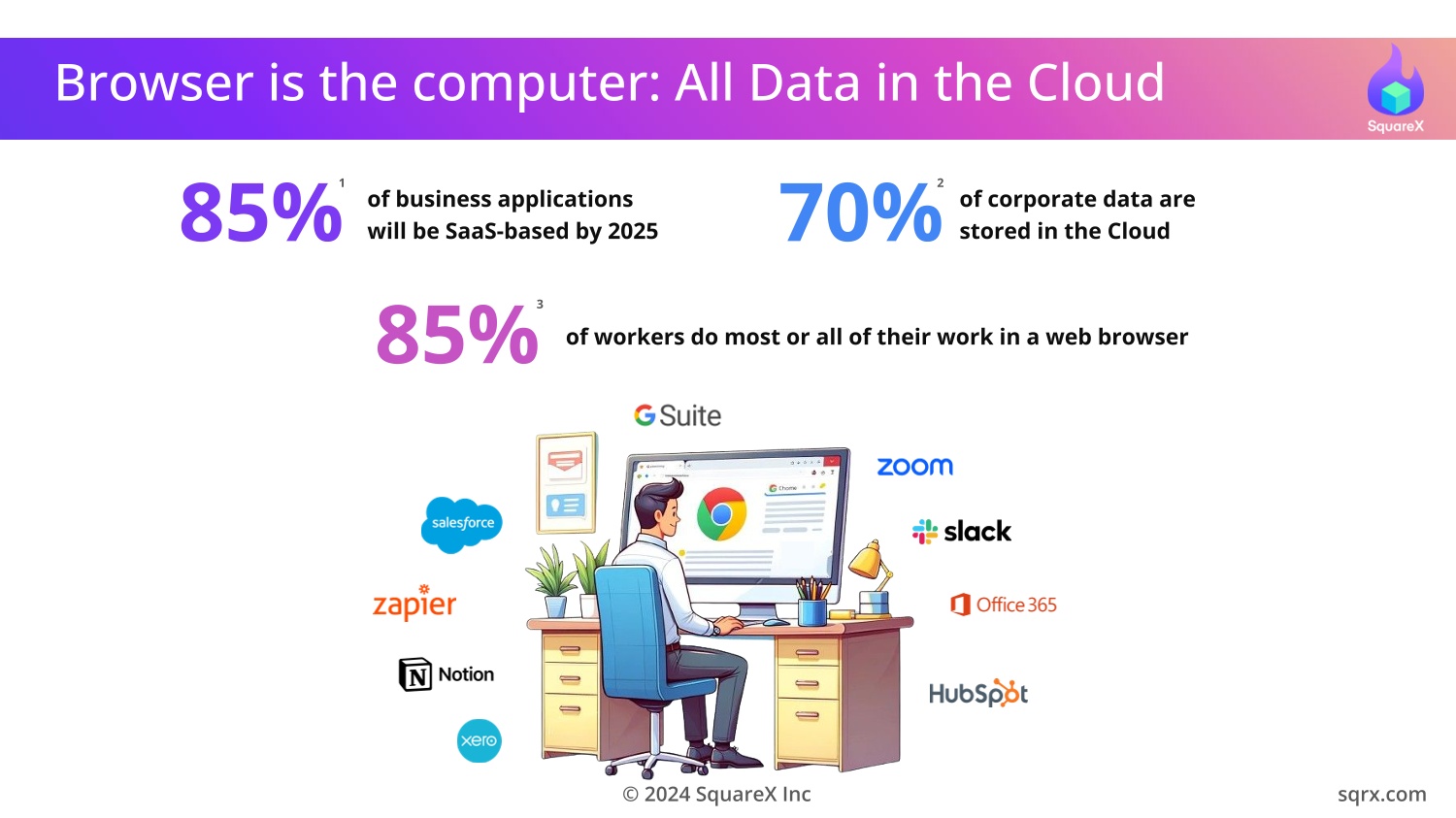
The web browser is the most used application within the enterprise
but also the least protected. Bad actors are now increasingly
targeting the weakest link: employees and consultants.
Unfortunately, most of these attacks happen online when the employee
or consultant is going about his daily work.
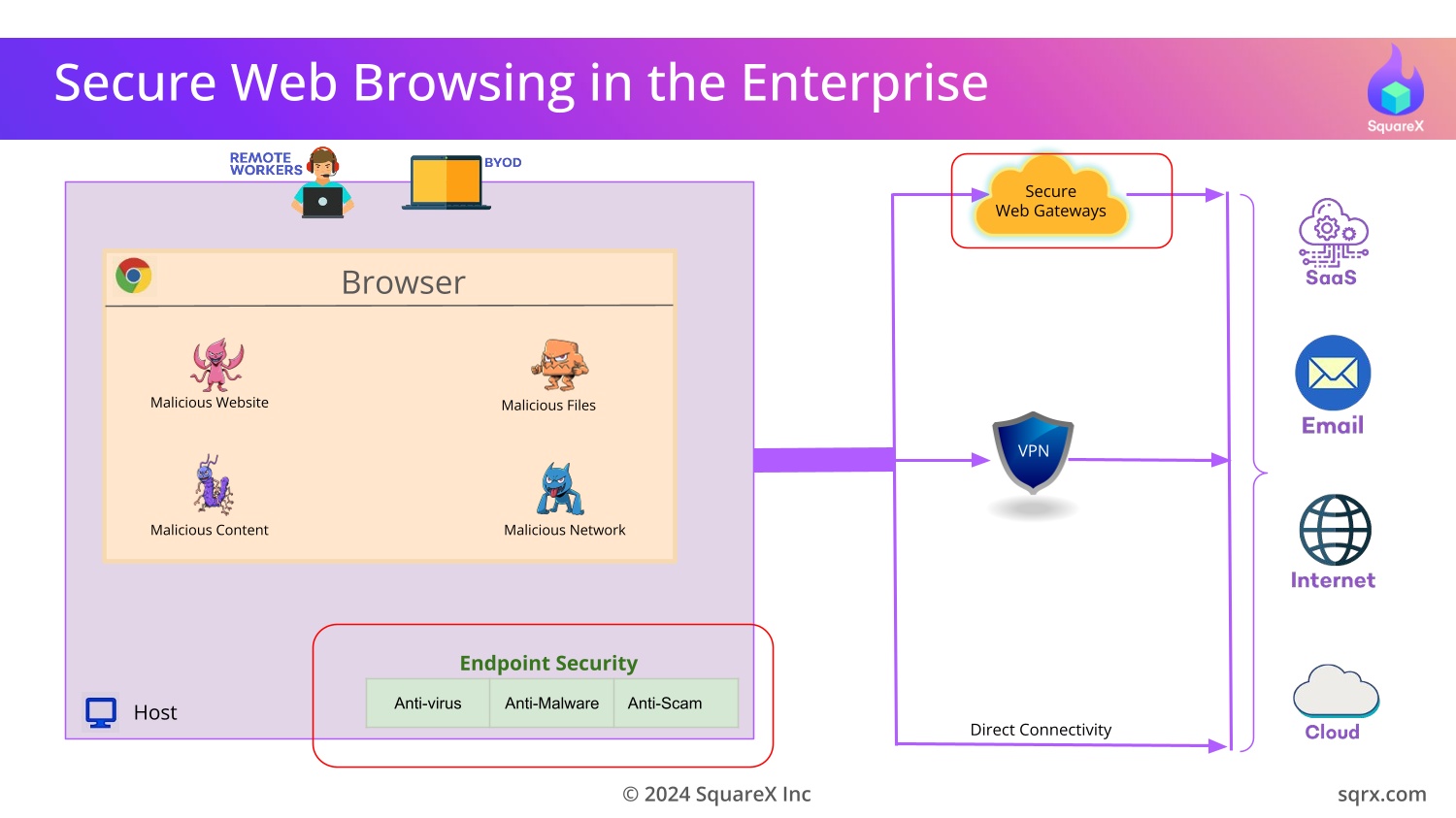
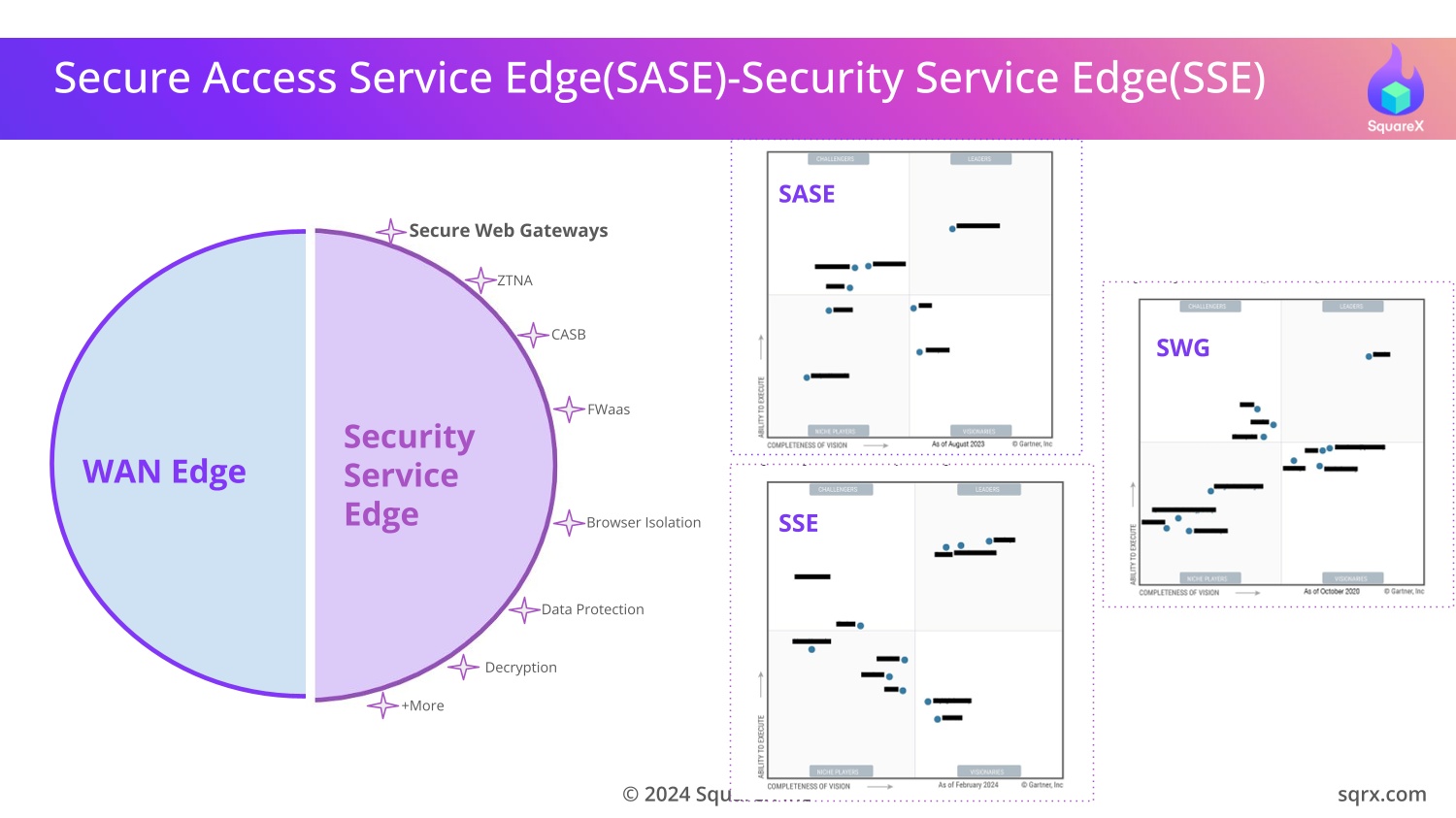
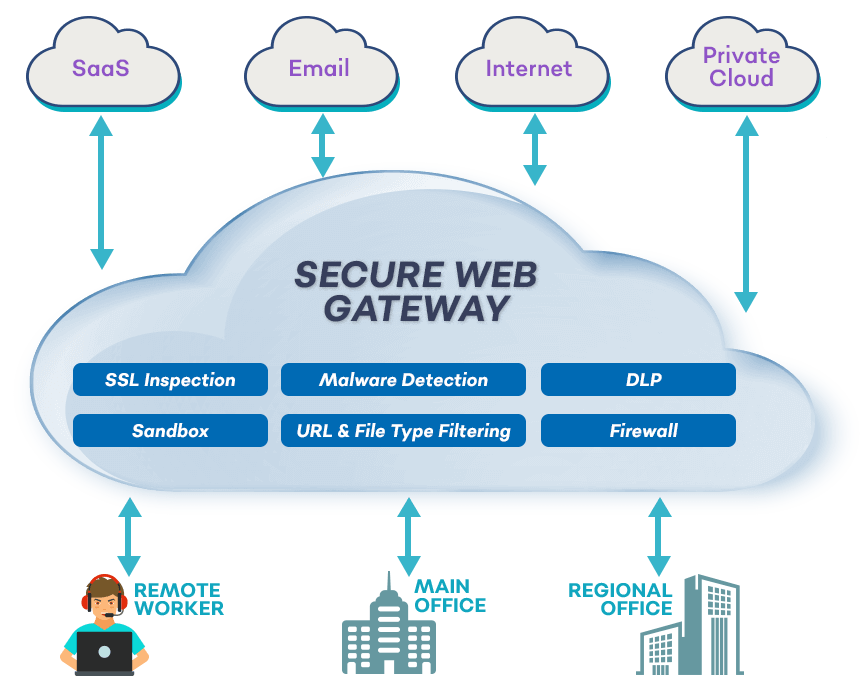
To counter these threats, security vendors have developed Secure Web
Gateways (SWGs) as part of Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) or
Security Service Edge (SSE) solutions to protect the browser.
However, this approach is fundamentally flawed because
these solutions are not equipped to detect attacks that occur on
the client-side.
The Last Mile Reassembly framework exposes a critical weakness in
these security solutions. By assembling the malicious payload
directly in the browser, these attacks bypass SWGs, no matter how
advanced their file scanning capabilities are, including heuristic
or AI/ML detection methods. Malicious files, instead of being
directly downloaded and scanned on the network, are smuggled through
the network and constructed within the browser. Similarly, malicious
websites are packaged into formats that SWGs typically ignore and
are then reassembled on the client-side, completely evading
detection.
All SASE/SSE vendors listed in the Gartner Magic Quadrant—who contribute to a Total Addressable Market of US$45 billion in
2023, forecasted to grow to US$80 billion by 2028—are affected by these attacks. Check if your SWG protects you against Last Mile Reassembly
Attacks here.
As Presented on DEF CON'32 Main Stage
Download Full Deck
Get your hands on the free copy of 'Breaking Secure Web Gateways for Fun and Profit' discussing architectural limitations of SWGs and how attackers are exploiting them.
Check your email inbox!
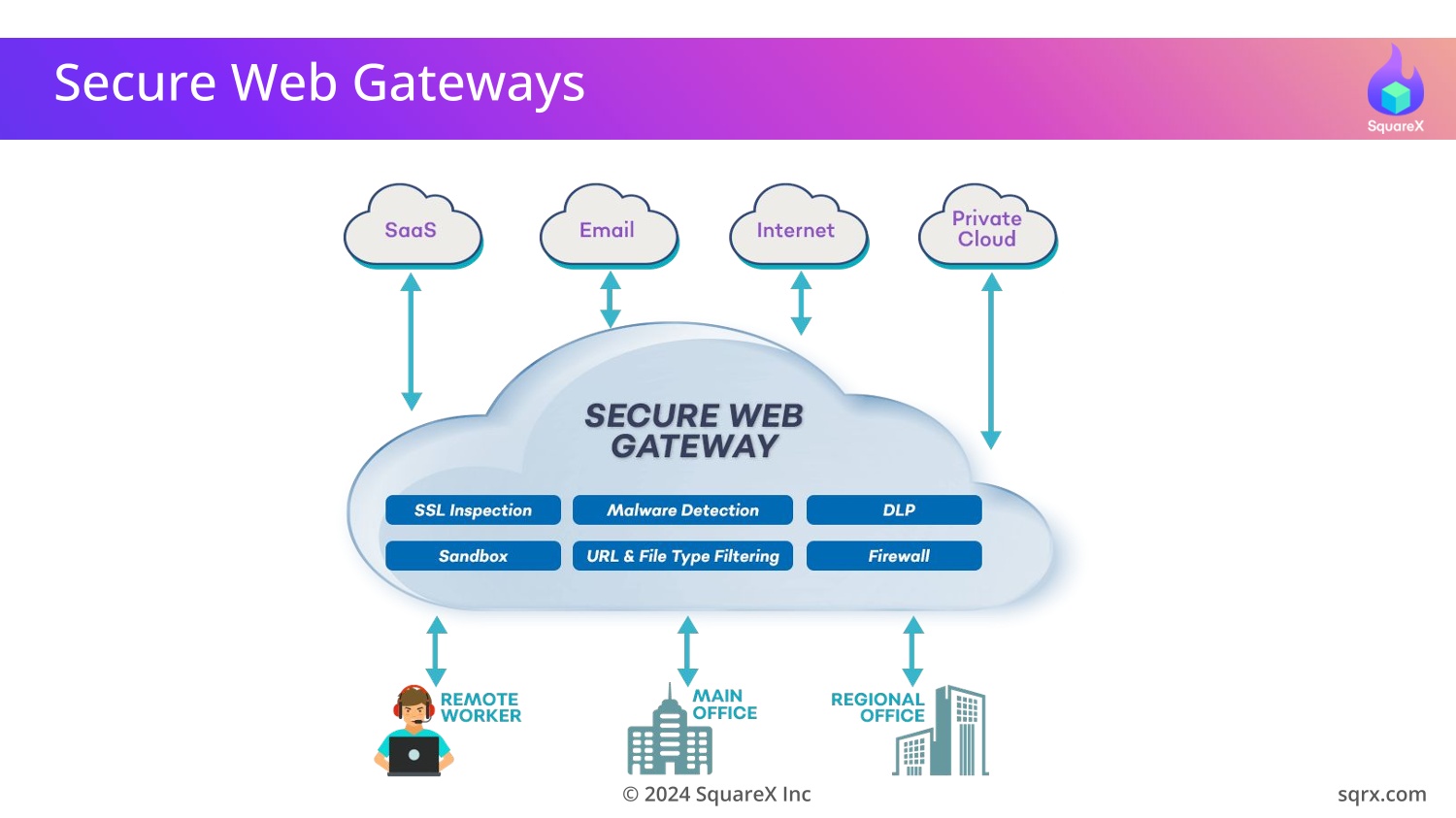
What do Secure Web Gateways promise?
Gartner's mandatory requirements for a SWG includes
malware protection, threat prevention, content inspection for
sensitive data, and URL filtering.
Many SWG vendors claim that they prevent 100% of all known malware and viruses embedded in websites from leaking through the web proxy.
However, SWGs have a fundamental architectural limitation: they only analyse data at the network level and have no awareness of what's happening on the browser. The Last Mile Reassembly Attack Framework exploits this vulnerability, effectively delivering known malware to the endpoints through the SWGs. This breaks most vendor SLAs!
Many SWG vendors claim that they prevent 100% of all known malware and viruses embedded in websites from leaking through the web proxy.
However, SWGs have a fundamental architectural limitation: they only analyse data at the network level and have no awareness of what's happening on the browser. The Last Mile Reassembly Attack Framework exploits this vulnerability, effectively delivering known malware to the endpoints through the SWGs. This breaks most vendor SLAs!
What SWGs can detect
SWGs analyze network traffic and look for signatures/patterns
of known malware and phishing websites.
SWGs also prevent sensitive data from being uploaded to unauthorized websites, by scanning a range of file types and file sizes for sensitive content. The limitations are publicly documented by each SWG vendor.
SWGs also prevent sensitive data from being uploaded to unauthorized websites, by scanning a range of file types and file sizes for sensitive content. The limitations are publicly documented by each SWG vendor.
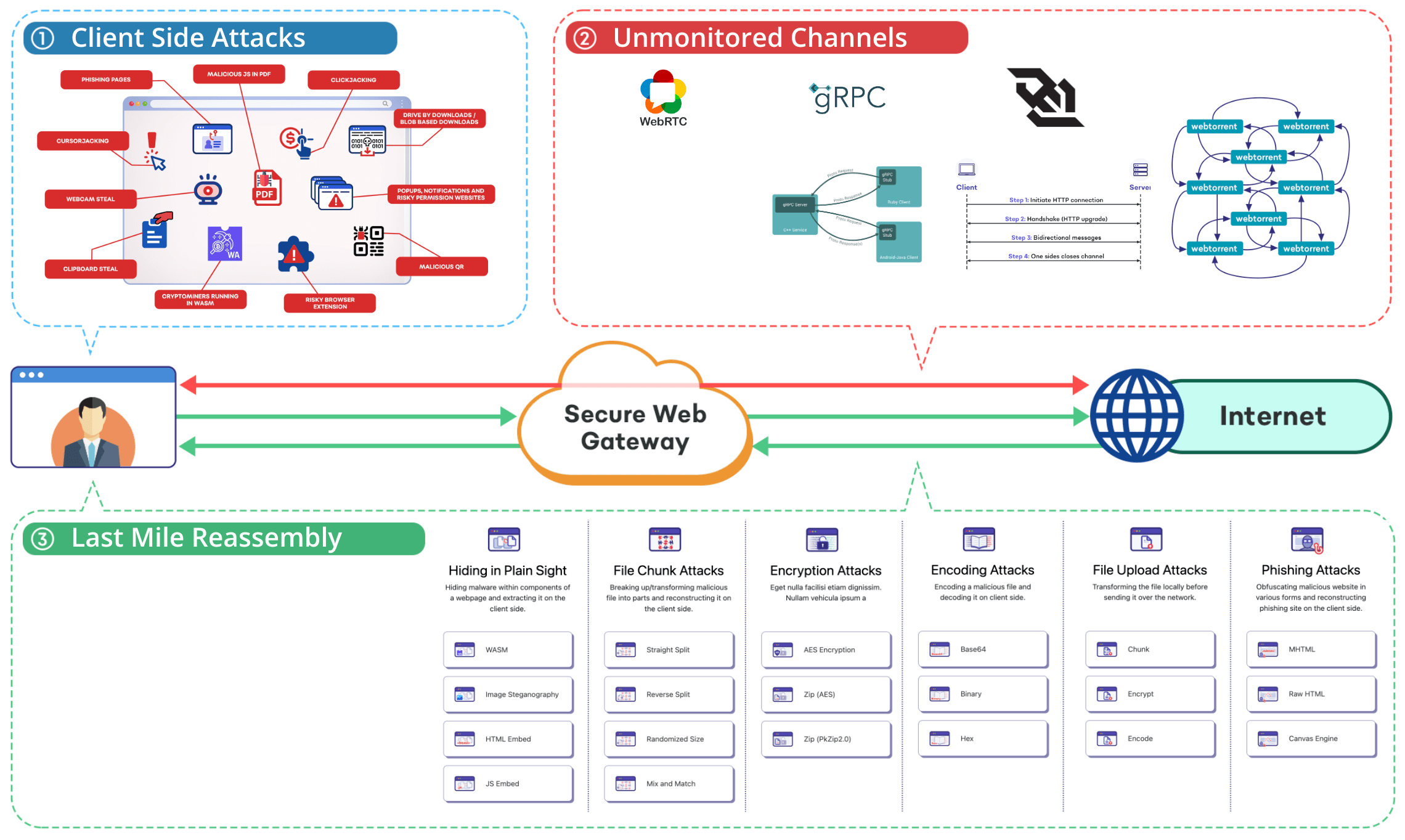
Where do Secure Web Gateways Fail?
No Web Application Context Awareness
No User Interaction Awareness
No Concept of Windows/Tabs
No Site Permissions Awareness
No Extensions Awareness
No Access to Rich Browser Metrics
This makes it easy for attackers to evade SWGs on many grounds.
1. Attackers can orchestrate a host of client-side attacks. These cannot be detected on the network layer.
2. Attackers can exploit channels that are unmonitored or difficult to monitor by SWGs.
3. Attackers can orchestrate any of the reassembly techniques on a website they control.
SWG Evasion Techniques
Smuggling Malware through Unmonitored Channels
SWGs do not support the inspection of certain protocols, and
their best practice often asks enterprises to block these
protocols entirely, which can hinder the functionality of
websites that rely on them. Examples include WebRTC,
WebSockets, WebTransport, and gRPC.
Attackers can exploit these channels to send malicious file
contents and drop the malware on the client-side.
Hiding in Plain Sight
Attackers can package malicious file contents inside
WebAssembly modules or other web resources like SVG, CSS, or
JS. They can also hide the malicious file inside an image
using steganography techniques. These are very difficult for
SWGs to detect.
A client-side JavaScript code can then extract the malicious
file from these resources and trigger a download.
File Chunking
As SWGs operate on the network level, they cannot
differentiate between windows and tabs.
In this attack, we break a file into different parts or chunks
and fetch them separately. The SWG sees multiple network
requests for these parts but doesn't realise that all these
parts will be reassembled in a single tab in a specific order.
The complete file will be malicious, but the individual parts
are not. On the client-side, JavaScript will reassemble these
parts in the correct order and trigger a malicious file
download.
Encryption / Decryption
In this attack, malicious file contents are encrypted and then
transmitted over the network. The SWG doesn't know the
password or the key needed to decrypt the data. The password
is embedded inside the Javascript code. On the client-side,
Javascript decrypts the file and triggers a download.
To the end user, it won't seem like a password-protected file,
as the entire process happens automatically, but the malicious
file is still delivered.
Encode / Decode
Similar to the encryption attack, in this method, the file is
encoded into a different format, such as base64, before being
transmitted. On the client-side, the file is decoded back to
its original form, and a download is triggered.
Bypassing File Upload Checks
The file upload bypasses involve all the aforementioned
attacks. As an example, a sensitive or malicious file is
broken into chunks before being uploaded. The SWG, which
operates at the network level, will not recognize that all
these chunks are being uploaded through the same tab, thereby
bypassing malicious file upload and DLP (Data Loss Prevention)
checks.
Delivering Phishing Pages
In this scenario, the phishing page is constructed entirely on
the client-side and rendered on victim's screen.
One approach is to render an MHTML file, which contains a full
webpage and its resources in a single file. Another approach
involves using a Canvas Engine, where the entire phishing page
is painted on the client-side. These methods make it hard for
anyone to detect the deception on the network level.