The Evolution of Ransomware: Browser-Native Ransomware

Learn How SquareX's Browser Detection and Response (BDR) Stops Browser-Native Ransomware
Fill out the form to request an enterprise pilot. For direct inquiries, please email founder@sqrx.com.
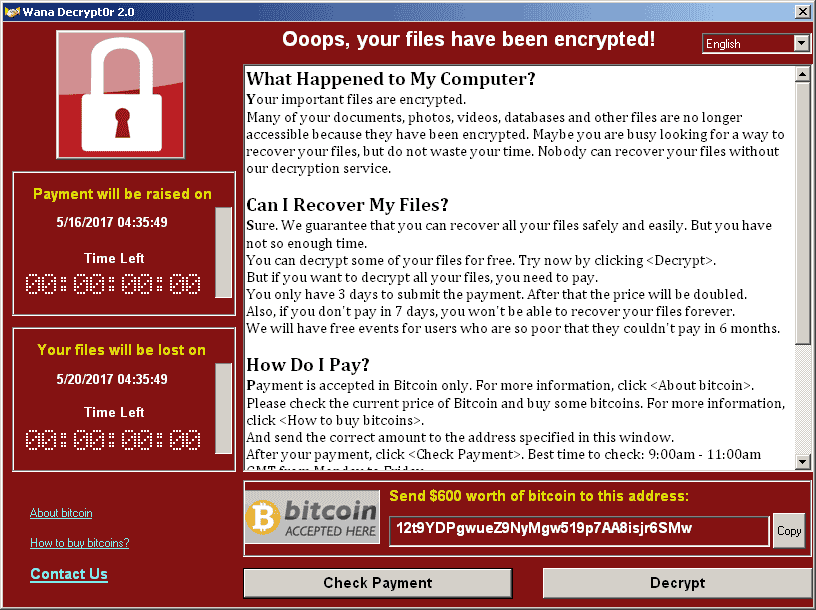
How Traditional Ransomware Works
Ransomware, a portmanteau of “ransom” and “malware,” is a type of malicious software designed to block access to a computer system or data until a ransom is paid. It typically involves three steps:
- Infection: Attackers trick victims into downloading and executing the ransomware through various attack vectors, such as phishing emails and malvertising campaigns.
- Data Encryption or Deletion: The attacker either encrypts or exfiltrates and deletes all data on the device, preventing the victim from accessing their files.
- Ransom Solicitation: Attackers demand payment, typically in cryptocurrency, in return for the decryption key or stolen data restoration.
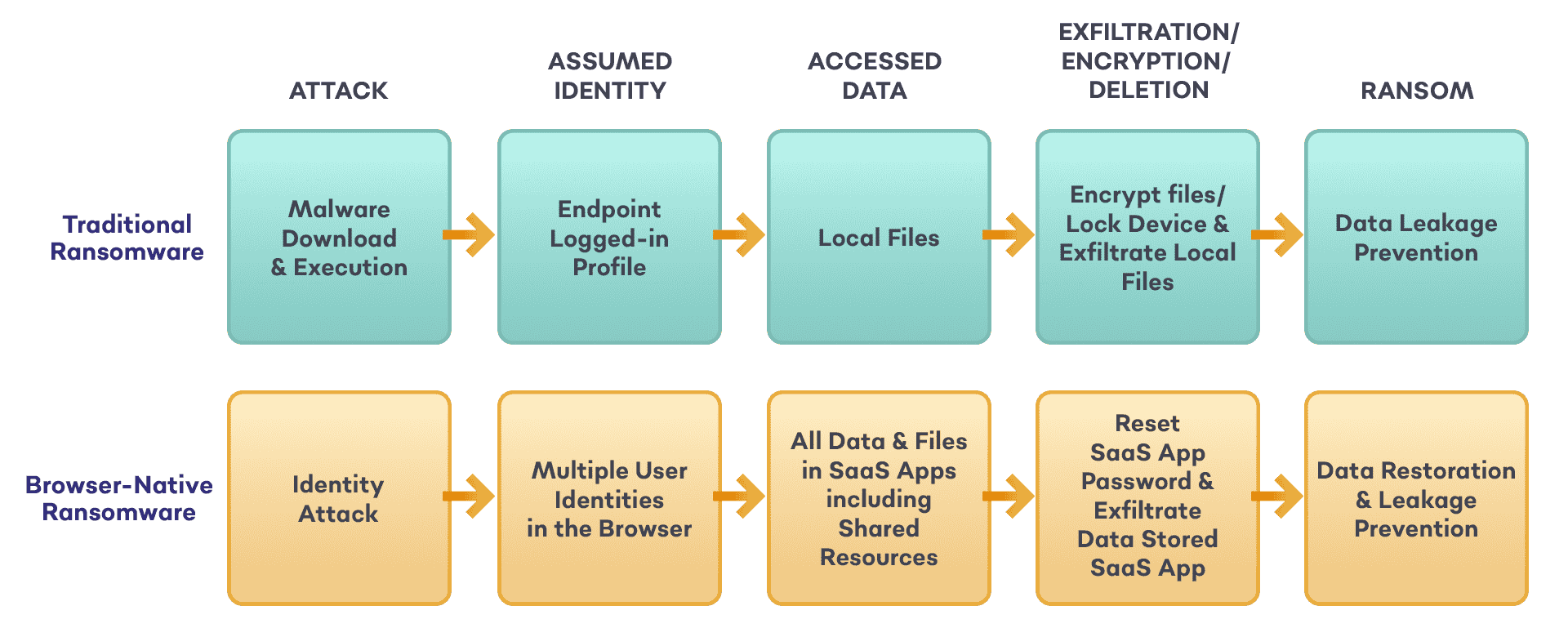
The Evolution of Ransomware is in the Browser
Most enterprise data today resides within SaaS applications. Unlike traditional ransomware that relies on file execution, browser-native ransomware exploits identity-based attacks to gain unauthorized access. Here's how it happens:
- Identity Attack: Attackers compromise victims’ credentials through various identity-based exploits such as consent phishing, browser sync-jacking, and polymorphic extensions.
- Data Exfiltration & Deletion: Using stolen credentials, attackers log into the victim’s SaaS apps, log them out, exfiltrate, and delete valuable information.
- Ransom Solicitation: Attackers demand payment in exchange for returning or withholding the leaked data.
Browser-Native Ransomware Case Studies
File Storage Browser-Native Ransomware
Email Browser-Native Ransomware
Browser-Native Ransomware via Browser Syncjacking
Security Challenges in Detecting & Mitigating Browser-Native Ransomware
Brand New Attack Surface
Compared to the endpoint, the browser is still a relatively nascent attack surface. Identity attacks are frequently delivered through newer attack vectors such as browser extension and OAuth authentication systems that remain poorly understood and managed.
Difficulty in Detecting an Ongoing Attack
For traditional ransomware, a malicious file or code will eventually be executed in the device, which is typically managed by the enterprise. In contrast, browser-native ransomware can target the victim’s identity in any SaaS application, including personal accounts or shadow SaaS apps that are not managed by the security team.
Existing Tools have Limited Visibility in the Browser
While EDRs play a critical role in defending against traditional ransomware, they work by inspecting malicious files and processes in the endpoint. Browser-native ransomware solely operates in the browser without involving any file download/native processes, and thus will never trigger any EDR inspection. Similarly, SASE/SSEs work by inspecting the proxy layer to infer application layer attacks and has poor visibility into the browser.
Lack of Browser-native Security Tools
Given the nativity of the space, most enterprises do not have the right browser-native tools to detect and mitigate browser-native ransomware. There is also no threat feed and limited attack documentation that security teams can rely on.
Lateral Movement via Shared Resources
One key benefit of using cloud services is the ability to collaborate and share resources with other individuals. For instance, an employee will have access to not only their own files, but any file on the company’s share drive to which they have access to. This makes lateral movement facile for browser-native ransomware. Where the impact of traditional ransomware is typically limited to the victim’s device, for browser-native ransomware, all it takes is one employee’s slip up to compromise the entire organization’s shared resources.
See what SquareX's bleeding-edge Browser Detection and Response (BDR™) solution can do for you.
See what SquareX's bleeding-edge Browser Detection and Response (BDR™) solution can do for you.
Given that browser-native ransomware fully operates within the browser, only a browser-native
security solution can defend against the attack.
SquareX’s industry-first Browser Detection and Response (BDR) solution detects, mitigates and
threat-hunt client-side web attacks targeting employees in real time. The solution comes in the
form of a lightweight browser extension that can be deployed to existing browsers via a simple
group policy.
- Web Threat Detection & Mitigation including identity attacks, malicious sites & scripts, malicious browser extensions and malicious files
- Browser DLP including genAI DLP, clipboard DLP, file DLP and insider attacks
- Private App Access to provide secure access to web applications and private apps via the browser, including for BYOD/unmanaged devices
SquareX’s BDR can detect and mitigate identity attacks, the initial access point for browser-native ransomware, including malicious extensions, shadow SaaS, OAuth scope management and advanced spearphishing attacks. For more information about SquareX’s BDR, contact us at founder@sqrx.com


